As the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries increasingly turn to data-driven solutions, the integration of real-world data (RWD) into regulatory decision-making has emerged as a key focus for enhancing pharmaceutical practices. Utilizing data from Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and medical claims can provide valuable insights into patient care and treatment outcomes. This strategy has the potential to transform the landscape for pharmaceutical manufacturers and regulatory service providers by helping to optimize drug development and improve patient access to medical products.
Real-World Data in Regulatory Context
Real-world data represents health-related information gathered outside traditional clinical trials, capturing the nuances of patient experiences within natural care settings. EHRs and claims data are two primary sources that capture this data, providing insight into patient demographics, treatment histories, and health outcomes. By converting this data into real-world evidence (RWE), regulatory bodies like the FDA can make more informed decisions about drug safety and efficacy.
EHR Data Life Cycle
One illustrative example from the document depicts the life cycle of EHR data (Figure 1). This life cycle encompasses multiple stages that convert raw data into structured data for research. Key phases include data capture, accrual, and transformation, each of which is subjected to quality checks to ensure data reliability and completeness, which are essential for regulatory submissions.
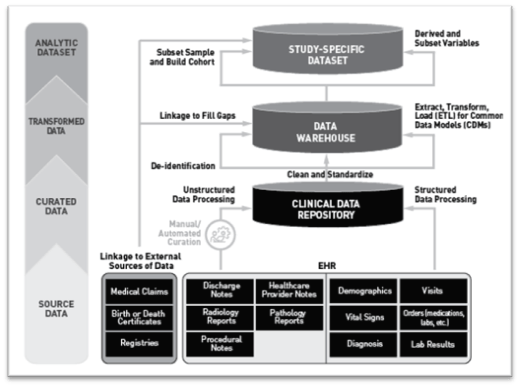
Figure 1: Life Cycle of EHR Data
(This diagram demonstrates the stages through which EHR data is processed, curated, and transformed into a format suitable for regulatory analysis)
Advantages of Using EHRs and Medical Claims Data
- Enhanced Patient Population Insights: EHRs and claims data provide a window into diverse patient demographics and varying healthcare experiences. These records can support more inclusive studies, enhancing the accuracy of product evaluations across different populations.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: RWD offers a pathway to reduce costs and time by providing access to pre-existing data on patient care and outcomes. This is valuable for manufacturers who need expedited insights for regulatory submissions or post-market studies.
- Improved Safety and Effectiveness Assessments: EHRs and medical claims data allow companies to analyze real-world outcomes, identifying potential risks and effectiveness metrics outside the controlled environment of clinical trials. For example, adverse events or treatment effectiveness can be observed in broader settings, allowing pharmaceutical firms to refine their product safety profiles and address patient needs more precisely.
Considerations for RWD Integration in Regulatory Decision-Making
Data Source Relevance and Selection
Selecting the right data source is critical for any regulatory study. EHRs and claims data must be carefully evaluated to ensure they provide relevant information, address study objectives, and capture accurate variables such as patient demographics, treatment specifics, and health outcomes. For instance, EHRs may lack consistency across healthcare facilities, while claims data might miss nuanced clinical details due to their billing-centric nature.
Data Quality and Completeness
Data quality and completeness are essential for regulatory use. RWD sources must be validated to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and traceability. The FDA recommends ensuring “data curation,” where patient data is harmonized across sources and structured to maintain integrity during analysis. For example, distributed data networks, which use a common data model (CDM), can enhance consistency across multiple sites by standardizing data formats.
Handling Missing Data and Validation Challenges
A recurring challenge in RWD studies is incomplete data capture. Gaps can arise if certain patient interactions are undocumented in EHRs or if insurance claims lack diagnostic accuracy. Utilizing data linkage techniques—such as combining EHRs with pharmacy records or laboratory data—can fill these gaps. Validation efforts are also important to ensure that recorded data aligns accurately with patient experiences, particularly for regulatory studies that focus on safety and efficacy outcomes.
Key Areas for RWD Application in Pharmaceutical Regulation
Post-Marketing Surveillance
RWD can enhance post-market safety surveillance by allowing continuous monitoring of adverse events and long-term drug efficacy in real-world settings. This extended observation is vital for adjusting dosage recommendations, identifying new risk factors, and making informed regulatory updates.
Efficacy and Safety Studies for New Indications
For pharmaceutical manufacturers exploring new drug indications, EHRs and claims data provide valuable insights into real-world treatment effectiveness. Using these sources, firms can conduct comparative effectiveness studies to show how new indications perform against existing standards of care, assisting regulatory agencies in the approval process.
Development of Predictive and Digital Health Tools
Incorporating real-world data into digital health tools, such as predictive algorithms for patient outcomes, can support patient-centered drug development. AI-driven analysis of RWD can identify patterns and predict responses to therapies, allowing pharmaceutical companies to refine drug formulations, optimize dosing, and personalize treatment plans for patients.
Challenges in RWD Integration
While RWD integration presents immense opportunities, it also raises concerns about data privacy, interoperability, and generalizability. Diverse EHR systems, for instance, may vary in how they capture patient information, potentially affecting data consistency across studies. Addressing these challenges will require collaboration between pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies to establish common standards and robust data governance practices.
In addition, advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning can help improve data processing capabilities, allowing for the efficient extraction of insights from unstructured EHR data. However, careful validation and regulatory oversight will be necessary to ensure these AI-powered methods produce reliable results for regulatory use.
Conclusion
Integrating RWD from EHRs and medical claims into regulatory practices offers a path to more flexible, patient-centered drug development. By incorporating this data, pharmaceutical firms can make data-driven decisions that align closely with patient outcomes, foster trust in the regulatory process, and streamline the path from clinical trials to patient care.
As regulatory agencies continue to evolve their standards, how do you see your organization adapting to the growing emphasis on real-world data?
Reach out to DDReg for expert regulatory services and tailored solutions for product registration in global markets. Read our blog – Navigating EU Classification Standards for AI in Medical Devices and Diagnostics

